The Role of OSHA: Ensuring a Safe Work Environment
Understanding what OSHA is, what businesses it regulates, and why, can keep both employers and employees safe at work.
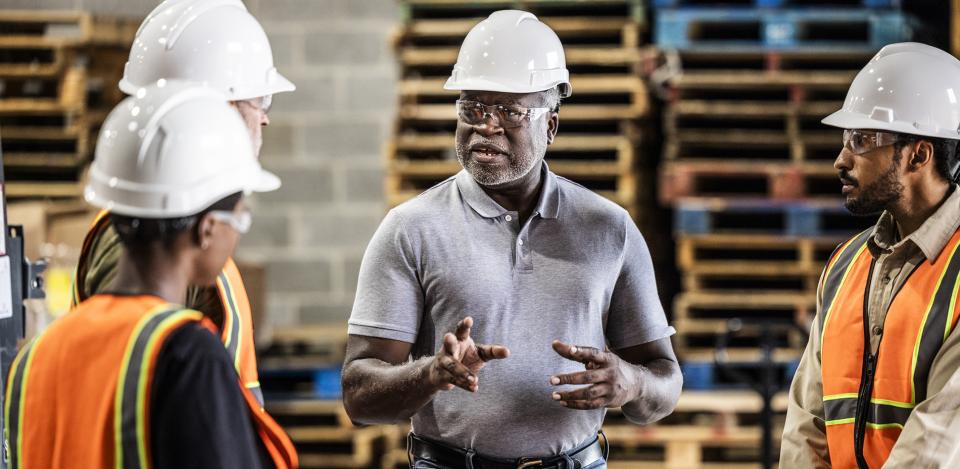

Whether a company has one employee or hundreds, few organizations are as vital as the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) when it comes to ensuring workplace safety. Understanding the role of OSHA can help both employers and employees maintain safe work environments, and gaining knowledge of workplace regulations and procedures is a valuable skillset whether your workplace is a construction site or a healthcare facility.
What Is OSHA?
OSHA is a federal regulatory agency that focuses on conditions in the American workplace. Its scope includes both the federal workforce along with most of America's private-sector employers
What is OSHA's mission? Simply put, this agency aims to ensure that American workers enjoy access to "safe and healthful working conditions" on the job. Additionally, OSHA strives to keep workplaces "free from unlawful retaliation," especially when workers speak up against unsafe or unfair workplace practices.
"OSHA is one of the most important drivers of Occupational Safety and Health in the United States," says Sean Castillo, a certified industrial hygienist with Georgia Tech Enterprise Innovation Institute. "The administration is a key force in the United States to protect the well-being and health of millions of workers in the country."
The Importance of OSHA
OSHA provides the accountability and support needed to improve safety for all types of workers and prevent them from being harmed. It serves as the foundation for a healthy and productive work environment through four key functions:
- Safeguards workers health and safety: By setting and enforcing workplace safety standards, OSHA helps reduce the risk of injury, illness, and death on the job. OSHA helps employers comply with these standards through access to training, and free on-site help for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Encourages workers to voice concerns. Another key function of OSHA is empowering workers to speak up about safety concerns without fear of retaliation. Employees have the right to request inspections, report hazards, and participate in investigations. This open communication helps identify risks early and supports continuous improvement in workplace practices.
- Boosts productivity and innovation: When safety and health protocols are followed and hazards are proactively addressed, businesses experience fewer disruptions due to accidents, medical leave, or regulatory penalties. OSHA’s guidelines support a more stable workforce by minimizing downtime and enabling employees to focus on their tasks with greater confidence and peace of mind.
- Mitigates risk in the workplace. By identifying potential hazards and requiring preventive measures, OSHA helps organizations avoid costly incidents, legal liabilities, and reputational damage. Its impact reaches beyond compliance; it builds the foundation for a safer, more resilient workforce.
What Does OSHA Do?
To fulfill its mission of securing a safe and healthy work environment, OSHA sets and enforces a variety of workplace safety and health standards. It also offers resources to help employers and employees make progress toward a shared goal of creating safe workplace environments.
"Besides enforcement actions, OSHA also conducts free compliance assistance measures, including safety and health training on selected topics to further employers and employees’ information on ways to stay safe in the workplace," Castillo says. "Across the United States, OSHA is involved in multiple partnerships and alliance programs with private and public organizations, including with general contractors on large-scale construction sites and the young worker initiatives. OSHA also funds the OSHA consultation programs in every state and territory of the United States, which provide free compliance assistance to small and medium-sized businesses."
Specific tasks and initiatives include:
- Issue regulations to address safety concerns. OSHA develops standards that employers must follow to protect workers from common hazards. These cover a lot of ground but often involve personal protective equipment, fall prevention, or hazard communication. New workplace developments may spark the need for new regulations.
- Enforce workplace standards. To hold employers accountable, OSHA conducts safety inspections, which involve in-depth systematic reviews of safety and health protocols and general workplace conditions. If employers fail to meet strict standards, OSHA may assess fines or citations. Employers may be required to take corrective action or could risk more severe penalties.
- Respond to employee requests for workplace inspections. Workers have the right to request inspections, especially if they express concerns regarding current health or safety practices within their work environments. Complaints can be filed anonymously, with each complaint evaluated thoroughly to determine whether onsite or offsite inspections are warranted. During these inspections, agency representatives, known as compliance officers, observe work practices, examine equipment, collect samples, and interview workers.
- Overseeing state-run programs. Many states have established their own safety plans. These must be approved by OSHA, which provides extensive oversight to ensure that state-based safety plans live up to high standards.
- Conduct whistleblower investigations. OSHA's Whistleblower Protection Program addresses concerns surrounding retaliation, particularly for workers who report concerns regarding workplace hazards or safety violations. The agency reviews these complaints and conducts whistleblower investigations to uncover signs of retaliation.
Which Businesses Does OSHA Regulate?
OSHA regulates most private sector employers and their workers across the United States, as well as some public sector employers. This includes a wide range of industries such as construction, manufacturing, warehousing, healthcare, agriculture, and retail.
Whether a company has one employee or hundreds, it is generally subject to OSHA regulations if it operates in the private sector. Employers are responsible for providing a workplace free from recognized hazards and complying with OSHA’s safety and health standards relevant to their industry.
However, there are some exceptions. OSHA does not cover self-employed individuals, immediate family members of farm employers, or certain industries regulated by other federal agencies — such as mining or transportation. Additionally, while OSHA sets guidelines for public sector employees, such as those working for state or local governments, enforcement in these areas depends on whether the state has an OSHA-approved State Plan. These plans must be at least as effective as federal OSHA and often extend coverage to public employees not covered by federal rules.
Georgia Tech’s Commitment to Worker Safety and Support
In addition to training professionals to prevent workplace injuries, Georgia Tech OSHA Training Institute Education Center (OTIEC) also supports families affected by workplace tragedies. Through a meaningful partnership with Kids’ Chance of Georgia, OTIEC donates a full program certificate in either construction or general industry safety and health for the silent auction held at the annual Georgia Safety, Health, and Environmental Conference. This event helps support Kids' Chance's mission to provide educational scholarships to the children of Georgia workers who have been seriously hurt or killed in work-related accidents.
One Georgia Tech student, Angela Juric, is an example of the positive impact the Kids' Chance scholarship can have on the child of an injured worker. Juric's father was catastrophically injured on the job when she was 11, changing both of their lives forever. As a Kids' Chance scholarship recipient, Juric now attends Georgia Tech and is using her education to become the medical resource her family needed during her father's recovery.
As Hilarie Warren, director of the Georgia Tech OTIEC, shared:
"Often, when people think of workplace safety or OSHA, they think of rules or laws. We must remember those rules were written as a result of immeasurable loss. They were established because every year, thousands of Americans died just going to work. Every one of those workers left family, loved ones, and a community behind. They left a story unfinished, but the Kids’ Chance scholarships provide an opportunity for these children and families to write another chapter."
Georgia Tech’s partnership with Kids' Chance of Georgia reflects its holistic approach to safety — one that values both prevention and compassion.
Explore OSHA Opportunities with Georgia Tech Professional Education
As a workplace safety manager or compliance officer, you have the power to make a difference on behalf of our nation's hardworking communities. Gain the insights and empowerment needed to drive change with the Professional Master's in Occupational Safety and Health (PMOSH) program at Georgia Tech.
"Professional education for safety health professionals, especially at Georgia Tech, allows for understanding and navigating the regulatory framework and standards of OSHA, as well as learning about the best practices of safety and health to go above and beyond the legal compliance," Castillo says. "Continued education allows for employees to conduct their duties with increased knowledge and confidence that will allow them to protect their employees and coworkers, and it can lead to increases not just in responsibility, but at times, upward mobility."
In addition to the PMOSH degree, Georgia Tech serves as an authorized OSHA Training Institute Education Center and offers professional development short-courses that can be taken either individually to advance skills and knowledge or completed as part of 11 OSHA certificates. Participants in a certificate program can choose classes from a variety of safety and health topics to meet their professional needs. Investing in your environmental, health, and safety leadership skills will protect employees and help grow your impact, benefiting your company.